Lidia Dragu
-
Particle Prague 2024
A week-long stay in Prague was organized for selected high school students, with this year’s program celebrating the 70th anniversary of CERN. Participants visited particle and nuclear physics labs, engaged with experts, and connected with peers who share similar interests. They gained firsthand experience in the life of a physicist through mini-projects in small groups,…
-
BeInspired@ICHEP2024
In celebration of CERN’s 70th anniversary and the ICHEP 2024 conference, a unique project was organized that brought together art, movement, and particle physics. Participants were inspired by particle physics to create their own artwork or movement choreography, which was then exhibited at two prestigious venues: the Prague Conference Centre during the ICHEP2024 conference from…
-
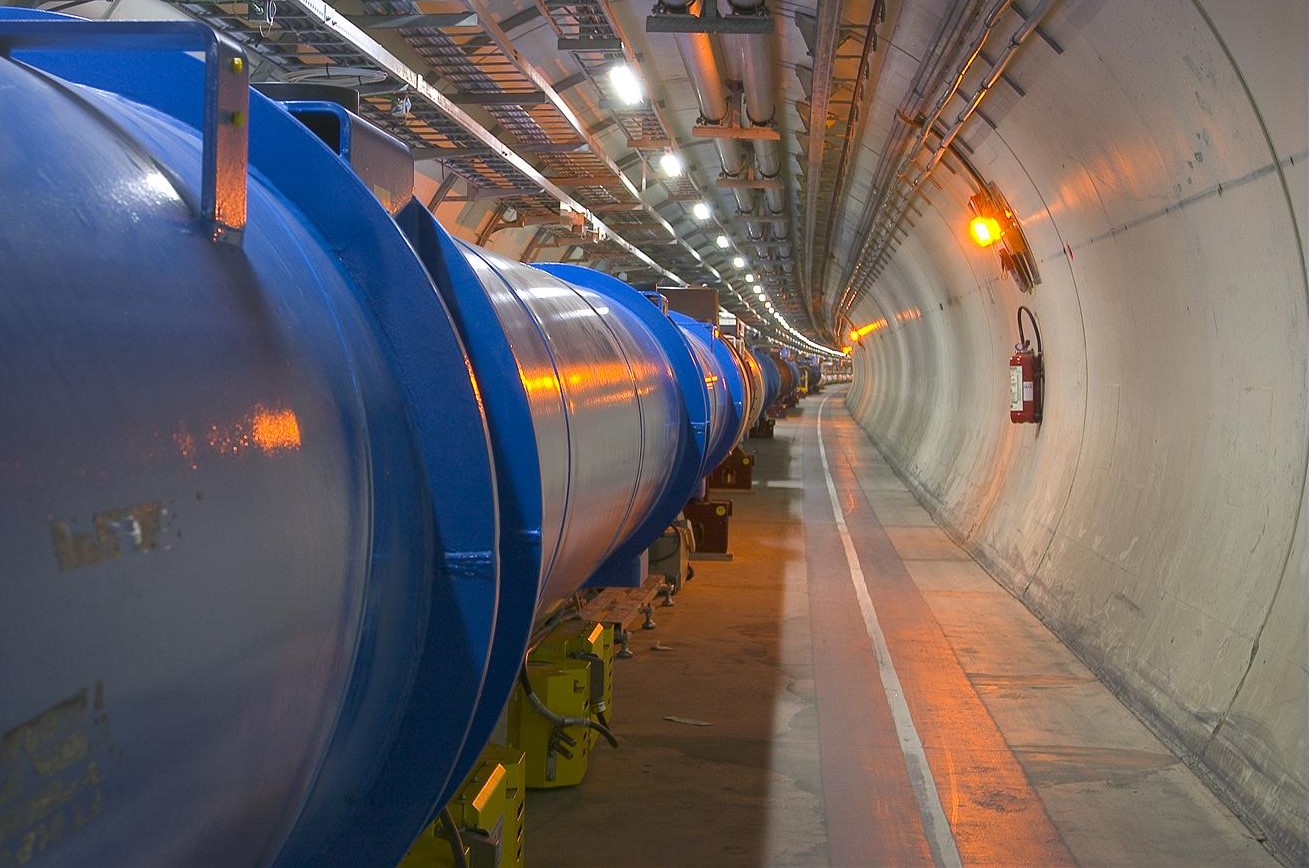
Switching on the Large Hadron Collider
The beginning of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) dates back to the early 1980s. CERN’s major accelerator, the Large Electron Positron Collider (LEP), was still in its study phase. But scientists were already considering using its 27 km tunnel for a proton collider. Hadron colliders were indeed extremely promising. CERN had developed revolutionary techniques with…
-
CERN70 in Germany Official Ceremony / Offizieller Festakt
On September 3rd, CERN’s seventieth anniversary was celebrated with a ceremonial event at the Futurium in Berlin. The event, held on behalf of the German CERN community, featured a diverse program focused on CERN’s scientific breakthroughs, its significance for technological innovations, and its contribution to international collaboration. Germany’s substantial role in the success of this…
-
Superconductors accelerate progress
The LHC, the largest superconducting machine in the world, demonstrates how particle physics and CERN have been a driving force in the development of superconductors. Superconductivity quickly emerged as a very useful property for high-energy physics. Since superconductors lose all electrical resistance below a certain, very low temperature, they are able to transport very high…
-
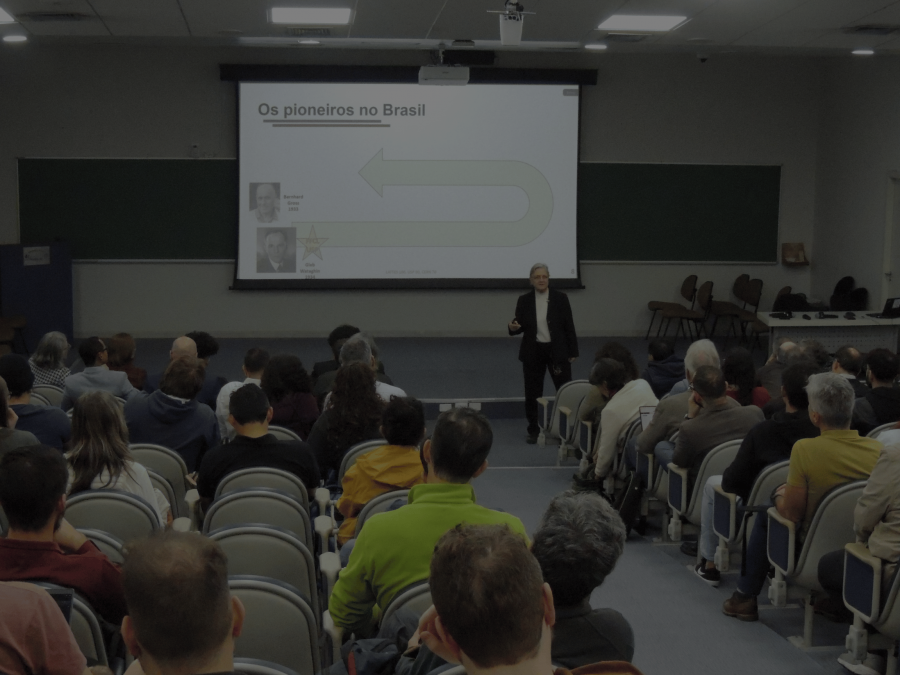
From cosmic rays to particle accelerators: 100 years of César Lattes, 90 years of University of São Paulo and 70 years of CERN
A series of anniversaries, from the creation of University of São Paulo to Brazil’s association with CERN, including the centenary of César Lattes, make 2024 a year in which Brazilian Physics celebrates its achievements. The purpose of the symposium was to bring together researchers in the field of High Energy Physics and interested parties in…
-
Into the antiworld
For each particle, there exists an antiparticle with opposite properties, in particular electric charge. This has been well established, ever since Paul Dirac’s theoretical predictions in the late 1920s. Over the three decades that followed, scientists discovered the constituents that would make up an antimatter atom: the antielectron (or positron), the antiproton and the antineutron.…
-
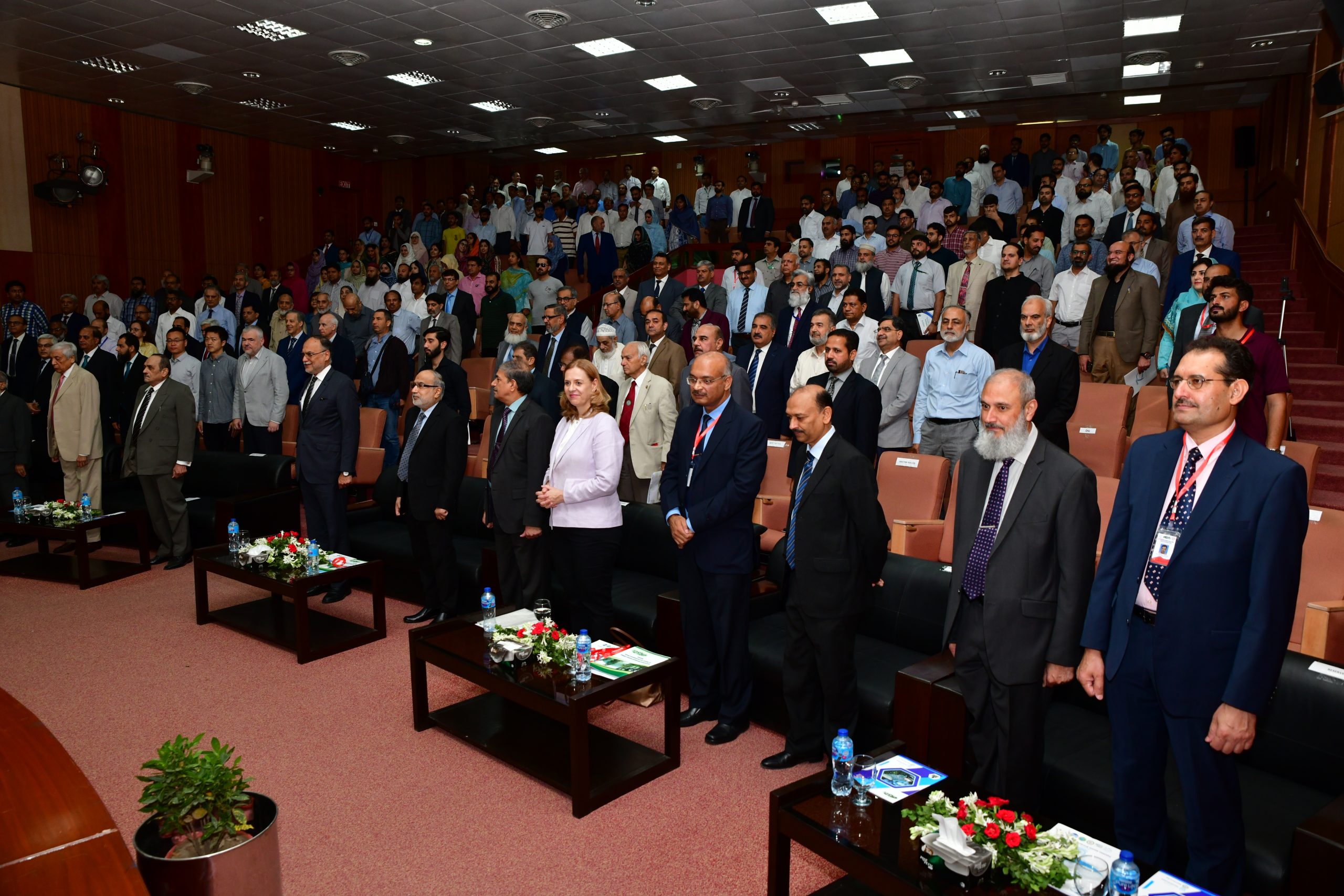
CERN70 and Pakistan
The CERN70 and Pakistan event, held in Islamabad on June 24-25, 2024, celebrated CERN’s 70th anniversary and marked 30 years of scientific collaboration between CERN and Pakistan. The inauguration ceremony commenced with a keynote address by Pakistan’s Minister for Planning and Development, Prof. Ahsan Iqbal, who emphasized the importance of international scientific partnerships. Dr. Raja…
-
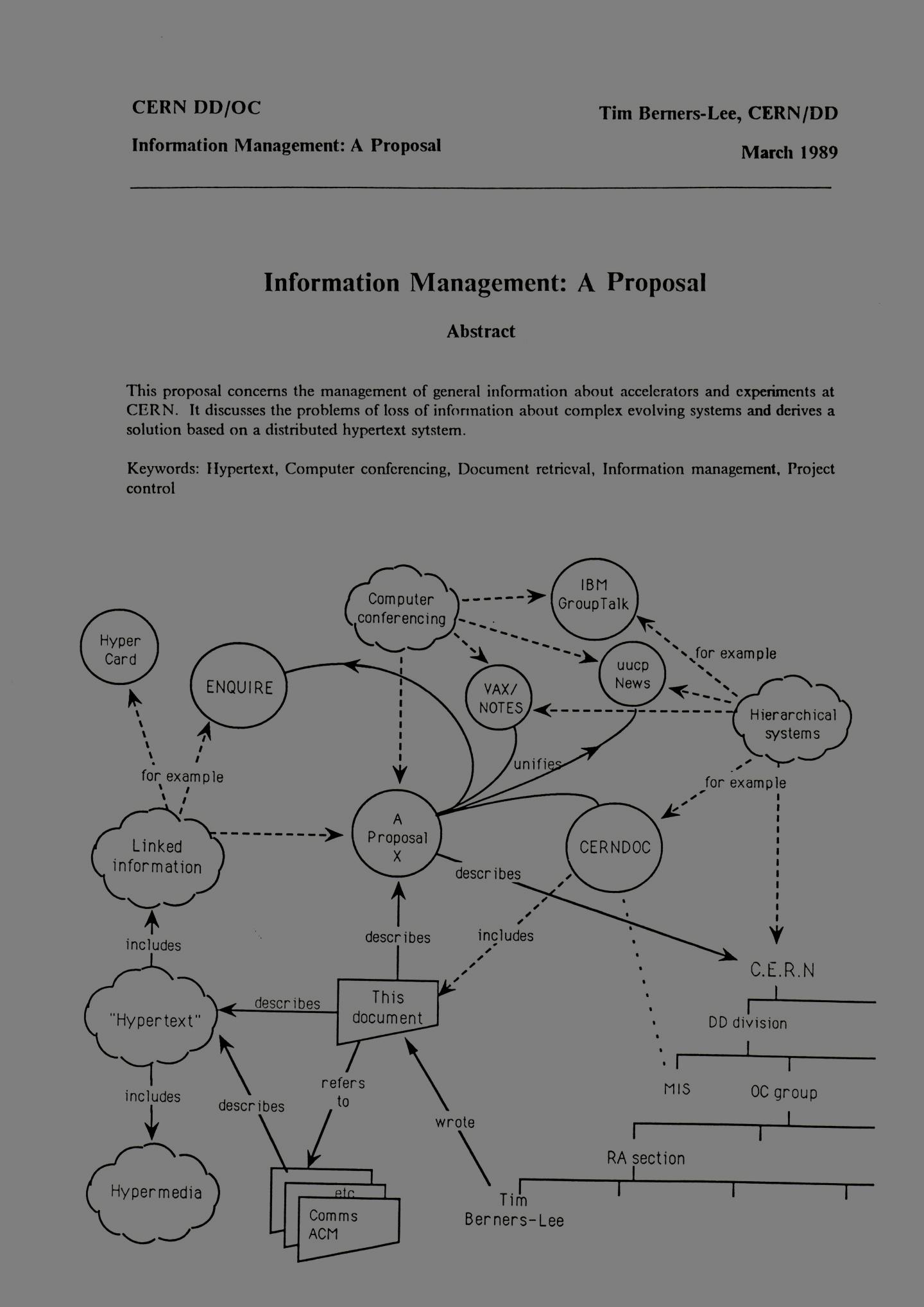
Where the Web was born…
In 1989, Tim Berners-Lee, a young scientist working at CERN, wrote a proposal for an information management system based on the Internet. At the time, few people really understood the significance of his seemingly abstract idea. Luckily, however, his supervisor and a few colleagues had the foresight to let him work on an invention that…
-
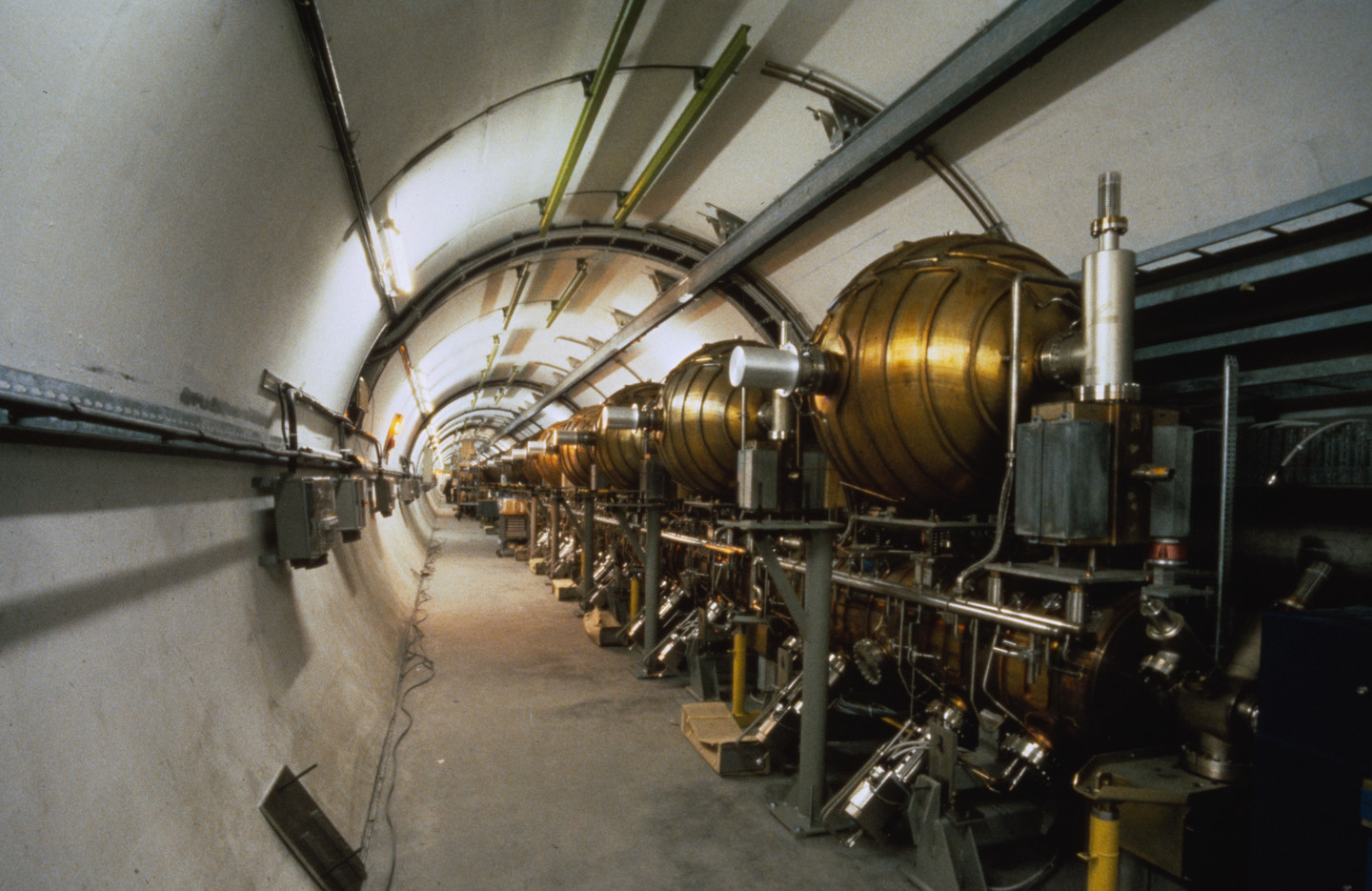
Green light for LEP
The Large Electron Positron collider (LEP) project was first presented to the CERN Council in June 1980, following the development of several concepts at different energies and lengths. The project envisaged an energy of 50 gigaelectronvolts (GeV) per beam and a circumference of 27 km, using the Proton Synchrotron (PS) and Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS)…